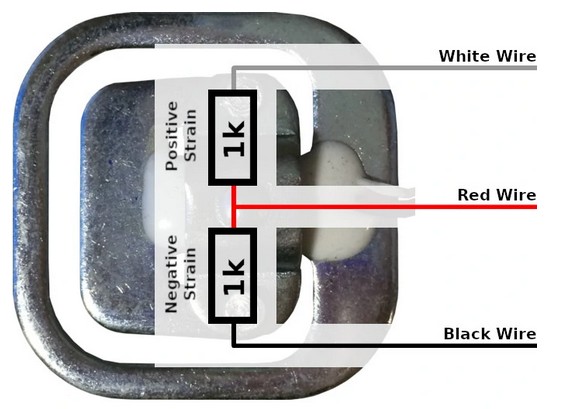
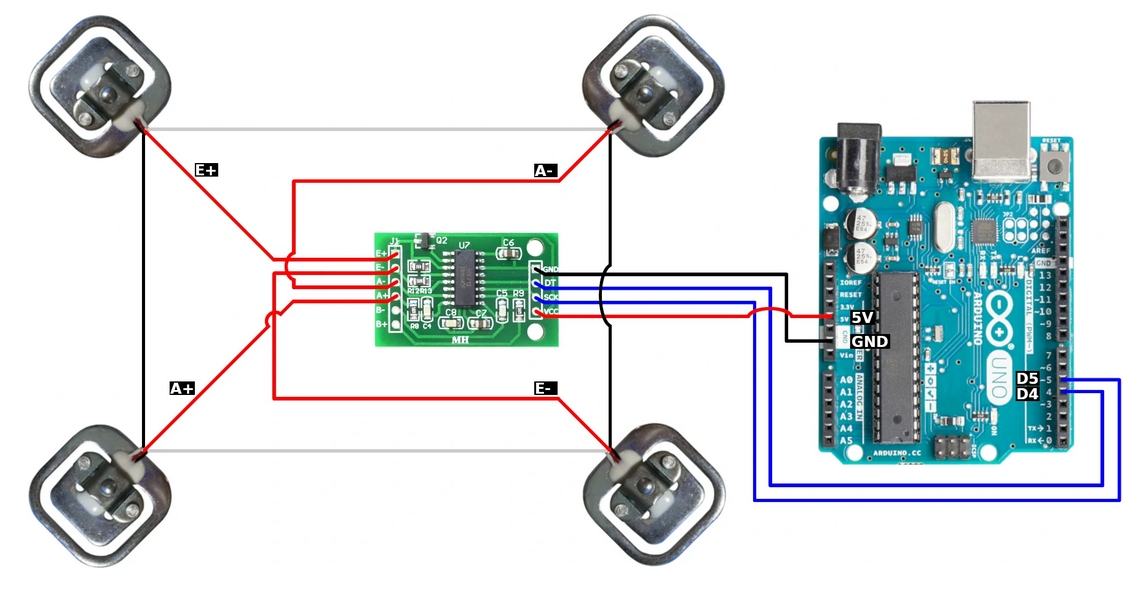
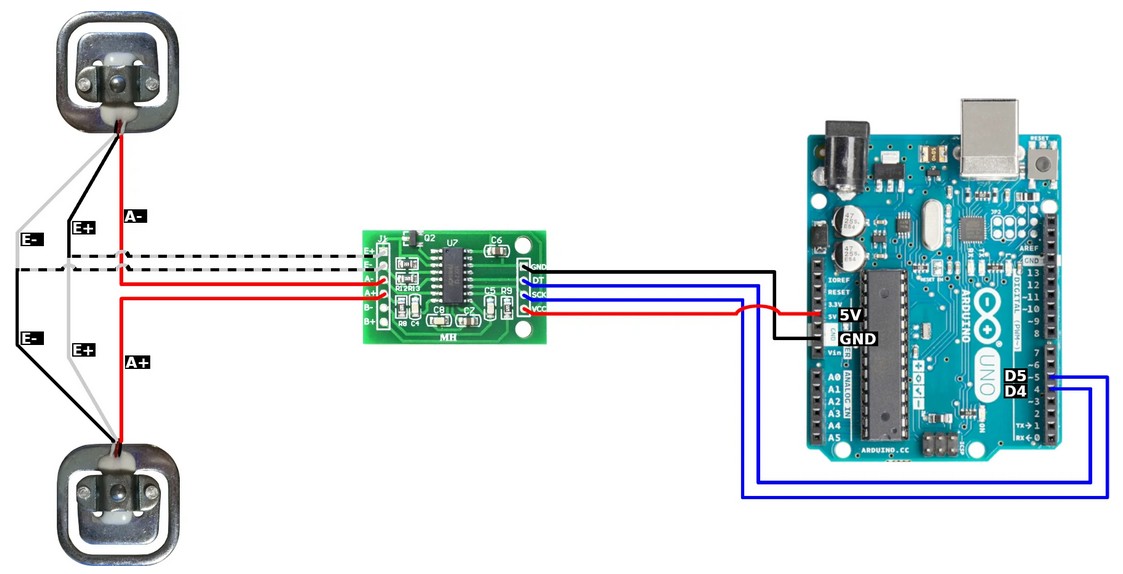
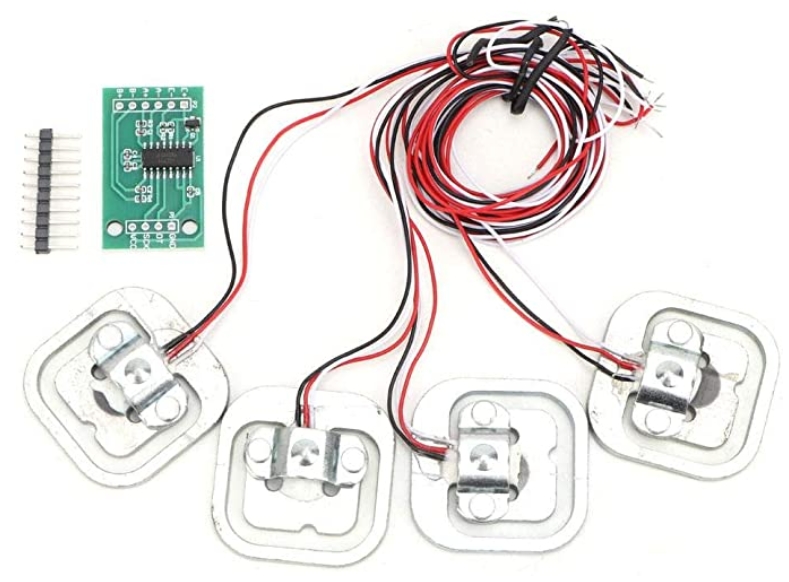
|
/*
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HX711_ADC
Arduino library for HX711 24-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter for Weight Scales
Olav Kallhovd sept2017
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*/
/*
This example file shows how to calibrate the load cell and optionally store the calibration
value in EEPROM, and also how to change the value manually.
The result value can then later be included in your project sketch or fetched from EEPROM.
To implement calibration in your project sketch the simplified procedure is as follow:
LoadCell.tare();
//place known mass
LoadCell.refreshDataSet();
float newCalibrationValue = LoadCell.getNewCalibration(known_mass);
*/
#include <HX711_ADC.h>
#if defined(ESP8266)|| defined(ESP32) || defined(AVR)
#include <EEPROM.h>
#endif
//pins:
const int HX711_dout = 4; //mcu > HX711 dout pin
const int HX711_sck = 5; //mcu > HX711 sck pin
//HX711 constructor:
HX711_ADC LoadCell(HX711_dout, HX711_sck);
const int calVal_eepromAdress = 0;
unsigned long t = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); delay(10);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("Starting...");
LoadCell.begin();
unsigned long stabilizingtime = 2000; // preciscion right after power-up can be improved by adding a few seconds of stabilizing time
boolean _tare = true; //set this to false if you don't want tare to be performed in the next step
LoadCell.start(stabilizingtime, _tare);
if (LoadCell.getTareTimeoutFlag() || LoadCell.getSignalTimeoutFlag()) {
Serial.println("Timeout, check MCU > HX711 wiring and pin designations");
while (1);
} else {
LoadCell.setCalFactor(1.0); // user set calibration value (float), initial value 1.0 may be used for this sketch
Serial.println("Startup is complete");
}
while (!LoadCell.update());
calibrate(); //start calibration procedure
}
void loop() {
static boolean newDataReady = 0;
const int serialPrintInterval = 200; //increase value to slow down serial print activity
// check for new data/start next conversion:
if (LoadCell.update()) newDataReady = true;
// get smoothed value from the dataset:
if (newDataReady) {
if (millis() > t + serialPrintInterval) {
float i = LoadCell.getData();
Serial.print("Load_cell output val: ");
Serial.println(i);
newDataReady = 0;
t = millis();
}
}
// receive command from serial terminal
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char inByte = Serial.read();
if (inByte == 't') LoadCell.tareNoDelay(); //tare
else if (inByte == 'r') calibrate(); //calibrate
else if (inByte == 'c') changeSavedCalFactor(); //edit calibration value manually
}
// check if last tare operation is complete
if (LoadCell.getTareStatus() == true) {
Serial.println("Tare complete");
}
}
void calibrate() {
Serial.println("***");
Serial.println("Start calibration:");
Serial.println("Place the load cell an a level stable surface.");
Serial.println("Remove any load applied to the load cell.");
Serial.println("Send 't' from serial monitor to set the tare offset.");
boolean _resume = false;
while (_resume == false) {
LoadCell.update();
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char inByte = Serial.read();
if (inByte == 't') LoadCell.tareNoDelay();
}
}
if (LoadCell.getTareStatus() == true) {
Serial.println("Tare complete");
_resume = true;
}
}
Serial.println("Now, place your known mass on the loadcell.");
Serial.println("Then send the weight of this mass (i.e. 100.0) from serial monitor.");
float known_mass = 0;
_resume = false;
while (_resume == false) {
LoadCell.update();
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
known_mass = Serial.parseFloat();
if (known_mass != 0) {
Serial.print("Known mass is: ");
Serial.println(known_mass);
_resume = true;
}
}
}
LoadCell.refreshDataSet(); //refresh the dataset to be sure that the known mass is measured correct
float newCalibrationValue = LoadCell.getNewCalibration(known_mass); //get the new calibration value
Serial.print("New calibration value has been set to: ");
Serial.print(newCalibrationValue);
Serial.println(", use this as calibration value (calFactor) in your project sketch.");
Serial.print("Save this value to EEPROM adress ");
Serial.print(calVal_eepromAdress);
Serial.println("? y/n");
_resume = false;
while (_resume == false) {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char inByte = Serial.read();
if (inByte == 'y') {
#if defined(ESP8266)|| defined(ESP32)
EEPROM.begin(512);
#endif
EEPROM.put(calVal_eepromAdress, newCalibrationValue);
#if defined(ESP8266)|| defined(ESP32)
EEPROM.commit();
#endif
EEPROM.get(calVal_eepromAdress, newCalibrationValue);
Serial.print("Value ");
Serial.print(newCalibrationValue);
Serial.print(" saved to EEPROM address: ");
Serial.println(calVal_eepromAdress);
_resume = true;
}
else if (inByte == 'n') {
Serial.println("Value not saved to EEPROM");
_resume = true;
}
}
}
Serial.println("End calibration");
Serial.println("***");
Serial.println("To re-calibrate, send 'r' from serial monitor.");
Serial.println("For manual edit of the calibration value, send 'c' from serial monitor.");
Serial.println("***");
}
void changeSavedCalFactor() {
float oldCalibrationValue = LoadCell.getCalFactor();
boolean _resume = false;
Serial.println("***");
Serial.print("Current value is: ");
Serial.println(oldCalibrationValue);
Serial.println("Now, send the new value from serial monitor, i.e. 696.0");
float newCalibrationValue;
while (_resume == false) {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
newCalibrationValue = Serial.parseFloat();
if (newCalibrationValue != 0) {
Serial.print("New calibration value is: ");
Serial.println(newCalibrationValue);
LoadCell.setCalFactor(newCalibrationValue);
_resume = true;
}
}
}
_resume = false;
Serial.print("Save this value to EEPROM adress ");
Serial.print(calVal_eepromAdress);
Serial.println("? y/n");
while (_resume == false) {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
char inByte = Serial.read();
if (inByte == 'y') {
#if defined(ESP8266)|| defined(ESP32)
EEPROM.begin(512);
#endif
EEPROM.put(calVal_eepromAdress, newCalibrationValue);
#if defined(ESP8266)|| defined(ESP32)
EEPROM.commit();
#endif
EEPROM.get(calVal_eepromAdress, newCalibrationValue);
Serial.print("Value ");
Serial.print(newCalibrationValue);
Serial.print(" saved to EEPROM address: ");
Serial.println(calVal_eepromAdress);
_resume = true;
}
else if (inByte == 'n') {
Serial.println("Value not saved to EEPROM");
_resume = true;
}
}
}
Serial.println("End change calibration value");
Serial.println("***");
}
|